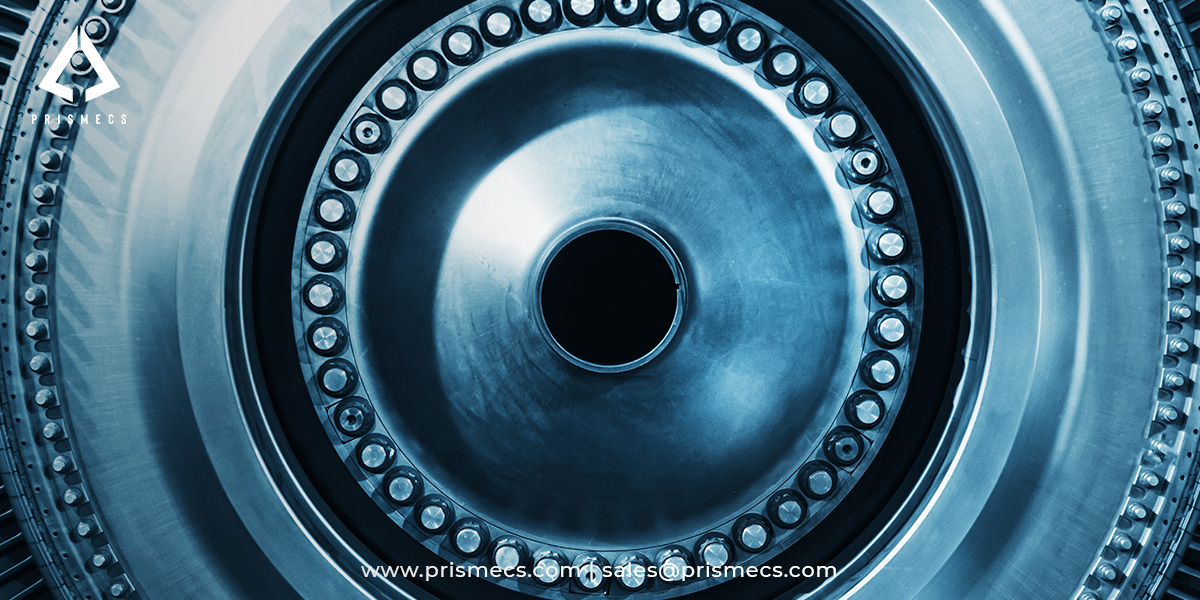
A gas turbine faces many operational problems. These are Rotor vibration, bearing failures, and Blade failures, but we will discuss only gas turbine bearing failures in this article.
Bearing failures are one of the common causes of turbine generator shutdown. While faulty design or manufacturing can be infrequently responsible, the most frequent cause of these failures is inappropriate operating conditions. Information given in this write-up will help you understand how many operating conditions affect bearing performance and what the operator can do to minimize the occurrence of bearing failures.
Common causes of Gas turbine bearing failure
A root cause analysis indicates that the leading causes of the bearing failure were mistakes made during the gas turbine overhaul and repair. They are primarily related to the inspection & quality checks carried out after the significant modification and alignment of the train modules.
A bearing failure happens when it fails to meet its expected life or performance stages, often causing a machine shaft to die. The machine it is a part of can break down or shut down.
You can see many causes of bearing failures, and few of them are more typical than others. More than 70% of bearing failures are because of poor fitting, lubrication, and contamination.
Let's deep dive into the following detail about these three typical reasons bearings fail as they relate to your gas turbine-related process.
Improper Lubrication
This should be one of the first and most common reasons when inspecting a bearing that has failed or is in distress. To provide proper lubrication, adequate viscosity at operating temperature is a necessity. While troubleshooting, you need to look for highly polished & discolored bearing raceways to evaluate if working surfaces lack acceptable viscosity at operating temperature. Although, over-lubricating can act just as detrimental as an under-lubricating process.
"Under-lubrication risks metal-to-metal contact. Over-lubrication becomes the cause of heat build-up & friction as the rolling components continuously try to push additional grease out of the way." according to IBT.
There are multiple causes of cage damage. Some of the more typical ones include vibration, extra speed, wear, or blockage. Also, many contaminants can become the reason for problems with a bearing. Dirt, sand, & water are the most common ones you run into. Still, chemicals & corrosives can also damage or stress your approaches.
These contaminants overcome viscosity which becomes the cause of corrosion to the bearing failure, disrupts the oil film, and causes erosion, leading to the generation of countless abrasive particles. Ensure to keep work locations, tools, fixtures, & hands clean, as this avoids contamination failures.
Misalignment
Misalignments lead to extensive vibration and loads. Few bearings (not all, though) can handle minor misalignments. The most usually found causes of misalignment include:
- Bent shafts.
- Dirt or burrs on the post.
- Housing shoulders.
- Shaft threads that are not square with shaft seals.
- Lock at the nuts along with faces that are not square to the thread axis.
To avoid misalignment, there are some of the best practices you can keep in mind. Ensure you inspect shafts & housing regularly, utilize precision-grade locknuts, and shim the accommodations as required.
How Industrial Operators Can Proactively Prevent Gas Turbine Bearing Failure
Preventing bearing failure requires more than routine inspection. In high-load industrial gas turbines, bearing reliability depends on precise lubrication control, shaft alignment accuracy, contamination prevention, and condition-based monitoring integrated into the plant’s maintenance strategy.
Operators should implement:
- Scheduled vibration and temperature trend analysis to detect early-stage bearing distress
- Lubrication quality monitoring, including viscosity, contamination levels, and oil film integrity
- Precision alignment verification after outages, overhauls, or component replacement
- Controlled storage and handling procedures to prevent premature bearing degradation
In utility-scale power plants and mobile turbine installations, these preventive practices significantly reduce forced outages and extend turbine operating life.
Prismecs supports power producers, oil and gas operators, and industrial facilities with gas turbine inspection, maintenance, spare parts supply, and reliability optimization services. Our field teams and engineering specialists help identify bearing risk factors early and implement corrective actions to maintain safe and continuous turbine operation.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the most common cause of gas turbine bearing failure?
Poor lubrication, contamination, and shaft misalignment are the leading causes. These conditions increase friction, wear, and reduce bearing life.
How does bearing failure affect gas turbine operation?
It increases vibration, damages rotating components, and can lead to unplanned turbine shutdowns.
What are the early warning signs of bearing damage?
Key signs include rising vibration, higher bearing temperatures, abnormal noise, and degraded lubrication oil.
How can operators extend gas turbine bearing life?
Use proper lubrication, ensure precise alignment, maintain cleanliness, and perform regular condition monitoring.
What is the normal operating temperature for turbine bearings?
Normal temperatures vary by design, but any unusual increase from baseline operating range indicates a potential problem.
Tags: gas turbine maintenance bearing failure analysis industrial turbine reliability turbine lubrication best practices gas turbine operation safety
recent posts

Data Centers
8 minutes read
Data Center Energy Efficiency Without the Outage Risk
Get data center energy efficiency and reliability, minus the outage risk. Trust our solutions to optimize your infrastructure. Contact us to get start...

Data Centers
14 minutes read
AI’s Rising Energy Demand - The Prismecs Strategic View
Discover strategic solutions for managing data center power demand driven by AI. Future-proof your infrastructure and minimize grid risks today.

O&M Services
13 minutes read
How to Choose Turbine O&M Services That Reduce Downtime
Learn how expert gas turbine maintenance protects uptime on General Electric fleets. See how Prismecs reduces risk and restores megawatts faster. Read...

Power Generation
10 minutes read
How to Maximize Uptime in Power Generation Plants
Discover how Prismecs power plant maintenance helps operators prevent outages, protect revenue, and keep turbines running at peak performance. Learn h...